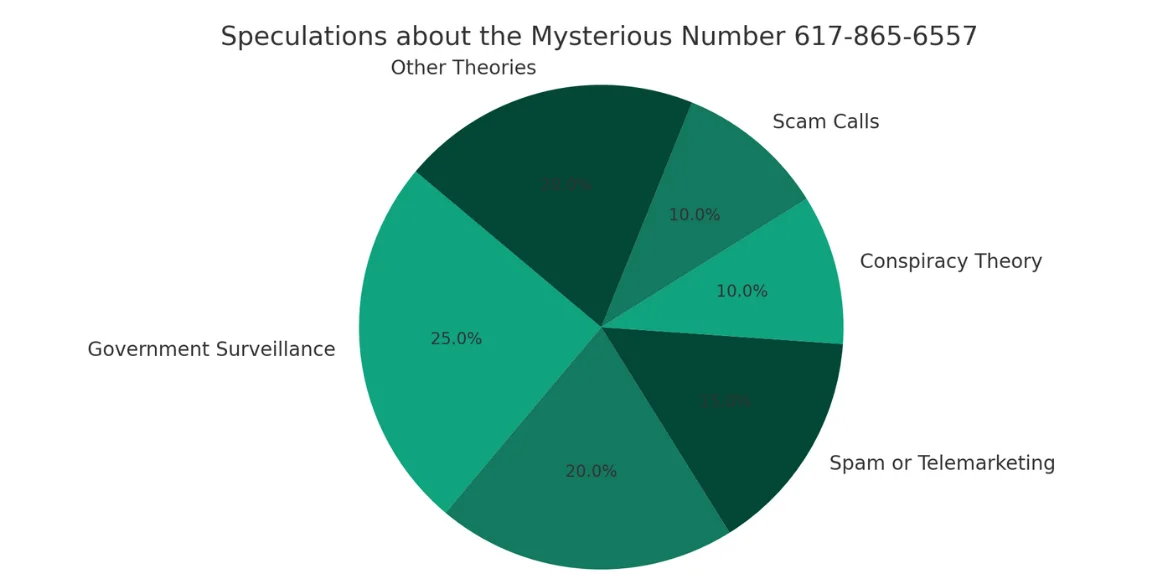
Search
Top Stories
Explore the latest updated news!
Stay Connected
Find us on socials
Made by ThemeRuby using the Foxiz theme. Powered by WordPress
Unlocking Business Success Through Email Marketing and SEO
Today's digital landscape requires businesses to implement effective marketing strategies that resonate with their target audiences. Understanding email marketing and…
Explore Top Categories
Uncover the stories that matter
Business
Uncover the stories that matter
Wanderlust
Let us be your guide to adventure
Don't Miss
Be the first to know
Latest News
Explore the Blog